Video recordings, especially from professional cameras for streaming devices, rely on different formats to store or transfer data properly. Many times, people notice large files with poor video quality and don't understand why it's happening. The reason mostly lies in the type of video compression being used in those media files. Similarly, missing support for a video's encoding method can cause playback to stop suddenly on computers or mobile devices.
This usually confuses users who don’t have much technical knowledge and forces them to look for ways to resume the playback. Therefore, this article will solve this confusion by providing a detailed H.264 vs MJPEG comparison. The contrast will help users learn about these encoder technologies and understand how they differ from one another. Additionally, you will know about a tool that fixes playback issues in videos regardless of their codecs.
In this article
Part 1. What Is H.264 and Its Key Characteristics
As a famous video compression format, H.264 reduces file sizes while retaining visual quality for playback. In the H.264 vs MJPEG comparison, this technology uses frame-to-frame prediction and motion compensation techniques to remove repeated data. This makes it more efficient than older compressions that process each frame separately. Many professional cameras and most streaming services use this encoding technology due to its balance of quality and size.
Key Characteristics of H.264
- Efficient Compression: It eliminates redundant visual data by analyzing changes between video frames using prediction methods. This enables it to achieve high video quality with significantly smaller file sizes compared to other formats.
- Compatibility: The encoding format is supported on most modern hardware and software, including smartphones and browsers. Users rarely need extra codecs or plugins to play this format across their devices.
- Variable Bitrate: It allows both constant and variable bitrate encoding options to match specific use cases such as streaming or local storage. Variable bitrate lets it adjust video data depending on the amount of motion or complexity in each section.
- Network Bandwidth: Due to its efficient compression, it requires less internet data during streaming or video conferencing. Thus, it enables smoother video compression, even over slower or limited internet connections.
Part 2. What is MJPEG and Its Key Features?
MJPEG is a video format where each frame is an individual compressed image. It was originally developed for video capturing and processing, especially in devices that could not handle complex compression algorithms. In the H.264 vs MJPEG comparison, it avoids inter-frame compression techniques and instead encodes every frame separately. While it simplifies decoding, it usually results in larger file sizes.

Key Characteristics of MJPEG
Compression: Each video frame is compressed as a separate JPEG image without relying on information from previous frames. This makes it easier for systems to decode the video without waiting for neighboring frames.
Storage Requirements: Since it doesn't reuse any image data between frames, its files are usually larger in size. This makes it less ideal for long video storage or streaming over slow networks.
Processing Load: The format puts minimal demand on device processors because each frame can be decoded individually. Consequently, even older or less powerful hardware can play MJPEG files without much delay.
Minimal Latency: Since there is no complex predictive encoding, it delivers video content with very low latency.
Part 3. H.264 vs MJPEG: A Detailed Comparison
To choose between H.264 vs MJPEG, this section covers the detailed table, highlighting its main aspects to make the finest choice:
| Feature | H.264 | MJPEG |
| Compression Type | Uses inter-frame compression by storing only the changes between video frames. | Uses intra-frame compression by saving each frame as a separate JPEG image. |
| File Size | Produces small files because it reuses data between frames. | Creates large files because it stores every frame fully |
| Video Quality | Maintains good quality even with smaller file sizes. | Offers good quality but needs more data to do so. |
| Latency | Has some delay due to how frames are decoded together. | Has low delay because each frame is shown instantly. |
| CPU Usage | Needs more processing power to compress and play videos. | Use less CPU power because it works with one frame at a time. |
| Streaming Flexibility | Works well for online streaming due to its smaller size and smooth playback. | Needs more bandwidth, making it harder to stream online. |
| Compatibility | Works with almost all modern devices and video platforms. | May not work on newer apps or websites without extra support |
| Bandwidth Use | Use less internet data, making it better for slow networks. | Uses more internet data and works best on fast connections. |
| Storage Space Needed | Saves more videos in less space due to strong compression. | Takes up a lot of space very quickly. |
| Encoding Speed | Slower to process video because it checks and compares many frames. | Faster to process video because it treats each frame on its own. |
Part 4. How to Choose Between H.264 and MJPEG for Different Applications?
Now that the difference is clear, let's see a few tips and suggestions in the following sections to better choose between H.264 vs MJPEG:
Storage and Length: You should use H.264 when streaming long videos or storing many recordings due to its smaller size and lossless quality. That’s because MJPEG files become very large over time as they store each frame individually.
Live Monitoring: Real-time applications that are used for security surveillance benefit more from MJPEG’s instant frame delivery and low latency. Since each frame is independent, there is no lag even if the system is under pressure.
Hardware Capability: Older system components usually lack support for decoding formats like H.264 properly. In these cases, MJPEG becomes a better option since it uses less CPU and requires no complex processing.
Video Editing: Editors mostly prefer MJPEG since each image can be edited without affecting other frames. Conversely, H.264 makes editing very hard since it compresses videos by linking multiple frames.
Network: H.264 works best where the internet speeds are limited, such as mobile networks or remote areas with weak signals. MJPEG requires more bandwidth, especially during continuous playback, which can cause frame skips.
Part 5. Fix Your Damaged or Unplayable Video Files Regardless of Codec with Repairit
Codec conflicts between H.264 vs MJPEG can result in damaged or unplayable video files. To cater to this, users can opt for Repairit, which is a dependable solution that repairs corrupted footage. This tool can fix videos across 25 video formats, including these two as well. Its advanced video repair technology uses AI to identify corrupted segments and quickly restore them using reference samples from an external media library.
Users can opt for this tool on the desktop to repair 8K videos with no size limits and can restore multiple files in one go with its batch repair. It can handle all video corruption scenarios, including power failure and editing crashes, restoring videos with precision and full playback quality. Moreover, the tool uses AI to unblur videos, enhance quality with sharp details, and colorize black-and-white footage into lifelike visuals.
Key Features

-
Gyroscope Data Repair: Users can restore GoPro gyroscope data with 98.15% accuracy, ensuring smooth playback and GyroFlow compatibility.
-
Professional Mode Video Repair: It can fix RAW and 4K videos and preserve original encoding by ensuring full compatibility with editing software.
-
LOG Data Repair: The tool restores video files shot from professional cameras using advanced codecs and maintains original metadata for seamless editing.
Fix Your Unplayable Video Files Regardless of Codec | Quick Tutorial
As discussed, this tool stands out for handling various video formats, including H.264 vs MJPEG. In the section below, we will discuss the detailed steps to use this advanced video repairing tool:
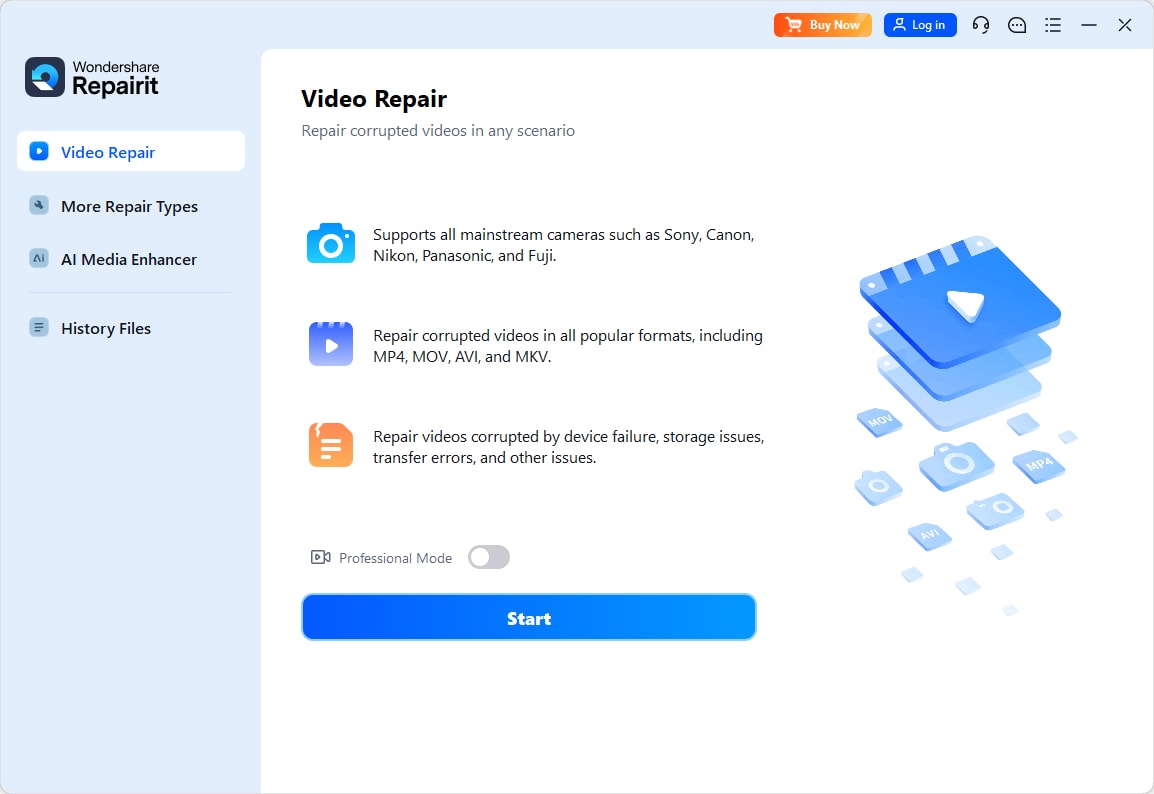
Step 1. Import Your Unplayable Video Files
Once the tool has been downloaded, access “Video Repair” and hit the “Start” button. Following that, opt for the “Add” button to import damaged video files.
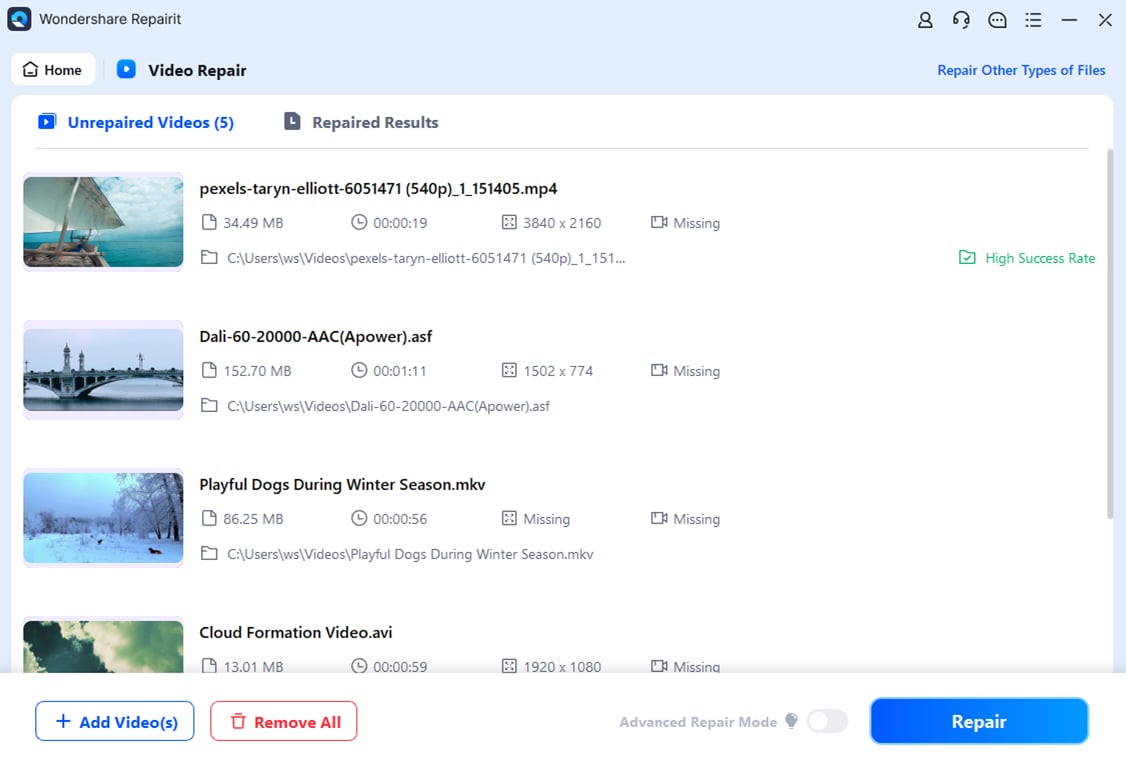
Step 2. Repair Your Damaged Video Files Regardless of the Codec
Once the files have been uploaded in the “Unrepaired Videos” section, select “Repair” to initiate the process of fixing.
Step 3. Export the Restored Unplayable Video Files
Within a few seconds, your videos will be repaired and can be downloaded to your devices using both the “Save All” and “Save” buttons.
Fix Your Damaged or Unplayable Video Files Regardless of Codec

Conclusion
To conclude, the H.264 vs. MJPEG comparison explains the differences between the two in terms of their ability to maintain video quality and size. Users who prefer high compression with better quality for streaming purposes can prefer H.264.
Similarly, MJPEG offers speed and easy frame access, making it ideal for security and editing purposes. Ultimately, they are advised to use Repairit to resolve codec issues and damaged videos.
Frequently Asked Questions
FAQ
-
Q1. Can MJPEG be converted to H.264 without losing quality?
Although you can convert the encoding of the video, it may result in minor quality loss. This happens because each frame is encoded again, which compresses it and results in quality loss. As losing quality is a part of this process, you can choose better export settings to minimize this loss significantly. -
Q2. Why does MJPEG need more bandwidth compared to H.264?
Since it compresses every frame individually without reusing any data, it increases the video size. Consequently, it means more data must be transferred over the network, which increases internet usage. Conversely, H.264 solves this by reusing image data between frames to reduce the transmission load. -
Q3. Can MJPEG be streamed over the internet like H.264?
Although streaming is possible, it is less efficient due to larger file sizes and more data in the frames. The high internet demand can result in slower loading times or buffering during playback. That’s one reason H.264 is preferred for smoother streaming over varying network conditions.

 ChatGPT
ChatGPT
 Perplexity
Perplexity
 Google AI Mode
Google AI Mode
 Grok
Grok