“H.264 vs H.265 picture quality. Would like to hear from anyone who has experience with both?”
Are you unsure whether to use H.264 or H.265 for your video quality needs? Discussing these two video compression technologies is a popular subject among videographers. H.264 has been the go-to format for technology professionals since it balances quality and file size demands well. Its successor, H.265, promises better compression and higher quality.
This article will explore H.265 vs H.264, focusing on their efficiency, quality, and specific use cases to help you decide.
In this article
Part 1. Understanding H264 and H265 Video Codec
Before comparing these two codecs, let’s briefly examine what they are about video compression factors. Additionally, see their related qualities in terms of streaming or recording activities.
1. H264
H.264 stands for Advanced Video Coding (AVC), one of the most commonly used standards for video compression online and by telecommunication gadgets such as smartphones or PCs. It was developed by the International Telecommunication Union (ITU) & International Organization for Standardization (ISO/IEC).
The entire industry adopted the standard for encoding videos due to its ability to produce high-quality video resolution at relatively low bitrates. Online streaming platforms, among other places, commonly use this form of video codec.
Benefits
- The great thing about H.264 is that it compresses high-resolution videos without losing quality. This makes it ideal for storage.
- There are numerous devices where H.264 works perfectly well, including smartphones, tablets, PCs, and smart TVs.
- The codec still maintains excellent video quality even with lower bitrates, which is a big deal for streaming services with low bandwidth.
- To achieve a smoother watching experience, H.264 has adaptive bitrate streaming. It adjusts the video quality resolution based on the viewer’s internet connection.
- It is good for live streaming and video conferencing due to its ability to resist errors. Thus more robustness against data loss and transmission errors.
2. H265
H.265 (High-Efficiency Video Coding) is also known as the successor of H.264 by the Joint Collaborative Team on Video Coding (JCT-VC). This was formed as a partnership between ITU and ISO/IEC.
The improvement in compression efficiency afforded by H.265 compared to H.264 permits better-quality videos at lower bit rates. This is particularly useful for 4K and 8K resolutions demanding applications and limited bandwidth network streaming.
Benefits
- It helps save storage space, which is vital, especially considering the amount of storage required for each HD movie consumed.
- It is more efficient when dealing with higher resolutions like 4K and 8.making it a better choice in ultra-high-definition video content production.
- With better compression algorithms, H.265 delivers enhanced video quality, particularly noticeable in scenes with high motion and complex textures.
- The codec's efficient compression reduces the data needed for streaming, allowing smoother playback and less buffering, especially on slower internet connections.
- H.265 contains HDR and adaptive bitrate streaming functionalities that optimize the viewer’s network condition and improve color depth, tone, and contrast.
Part 2. H264 vs H265: What’s the Difference?
Choosing between H.264 and H.265 can be challenging due to their distinct features and benefits. How do these video codecs differ regarding compression efficiency, file size, and video quality? What impact do these differences have on streaming, storage, and playback?
The table below provides a detailed comparison to help you understand the key differences and decide which codec best suits your needs.
| Attribute | H.264 (AVC) | H.265 (HEVC) |
| Year of Standardization | 2003. | 2013 |
| Compression Efficiency | Moderate | High (50-70% improved) |
| File Size | Larger | Up to 50% smaller for the same quality |
| Video Quality | High, but less efficient at higher bitrates | Higher, maintains quality at lower bitrates |
| Supported Resolutions | Up to 4. | Up to 8K and beyond |
| Processing Power Required | Lower | Higher |
| Encoding/Decoding Time | Faster, lower computational power required | Slower, higher computational power required |
| Intraframe Prediction Modes | 9 modes | 35 modes |
| Motion Compensation | Vector prediction | Advanced vector prediction |
| Color Depth | 8 bit | 10 bit |
| Compatibility | Widely compatible with older and newer devices | Increasingly supported, less backward compatible |
| Streaming Efficiency | Requires more bandwidth | More efficient, less bandwidth needed |
| Use Cases | Blu-ray discs, online streaming, video conferencing | 4K/8K streaming, UHD Blu-ray discs, high-quality broadcasting |
For the minimum upload speed, here are their differences:
| Resolution | H.264 (AVC) | H.265 (HEVC) |
| 480p | 15 mbps | 0.75 mbps |
| 720p | 3 mbps | 1.5 mbps |
| 1080p | 6 mbps | 3 mbps |
| 4K | 32 mbps | 15 mbps |
Part 3. How to Repair Corrupted H264 and H265 Videos?

-
Repair damaged videos with all levels of corruption, such as video not playing, video no sound, out-of-sync video or audio, playback errors, header corruption, flickering video, missing video codec, etc.
-
Repair full HD, 4K, and 8K videos and support 18 popular Codecs, including H264 and H265 etc.
-
Repair damaged or corrupted videos caused by video compression, system crash, video format change, etc.
-
Repair critically damaged or corrupted videos available on SD cards, mobile phones, cameras, USB flash drives, etc.
-
Repairit has a quick and advanced scanning mode. You can use either depending on the level of corruption the video file has undergone.
-
No limit to the number and size of the repairable videos.
-
Support Windows 11/10/8/7/Vista, Windows Server 2003/2008/2012/2016/2019/2022, and macOS 10.10~macOS 13.
If your videos aren't playing correctly, it could be due to issues with the video codecs or file corruption. Problems often arise when the codec used to create the video doesn't match your device's needs, or if the video file itself is damaged. Other times, your device might lack the necessary codec or have conflicting codecs.
When faced with these issues, Repairit Video Repair can help. This tool fixes broken videos in various formats, including H.264 and H.265, and supports many others like MKV, WMV, FLV, and MOV. Repairit can handle all levels of corruption, whether your video isn't playing, has no sound, is out of sync, or has playback errors.
If you're curious about how Repairit fixes corrupted video codecs, here are the steps:
Step 1: Download Repairit. Then, import your corrupted H 26.H 265 videos into the software using the +Add button.
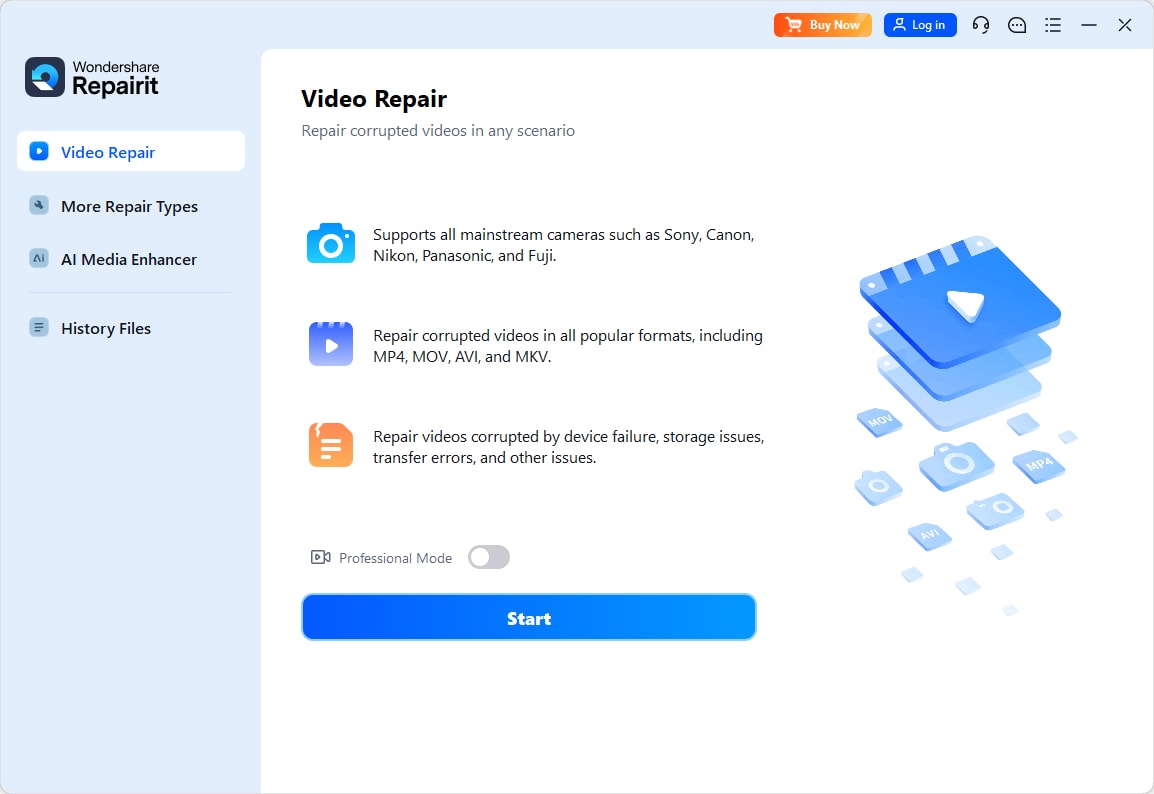
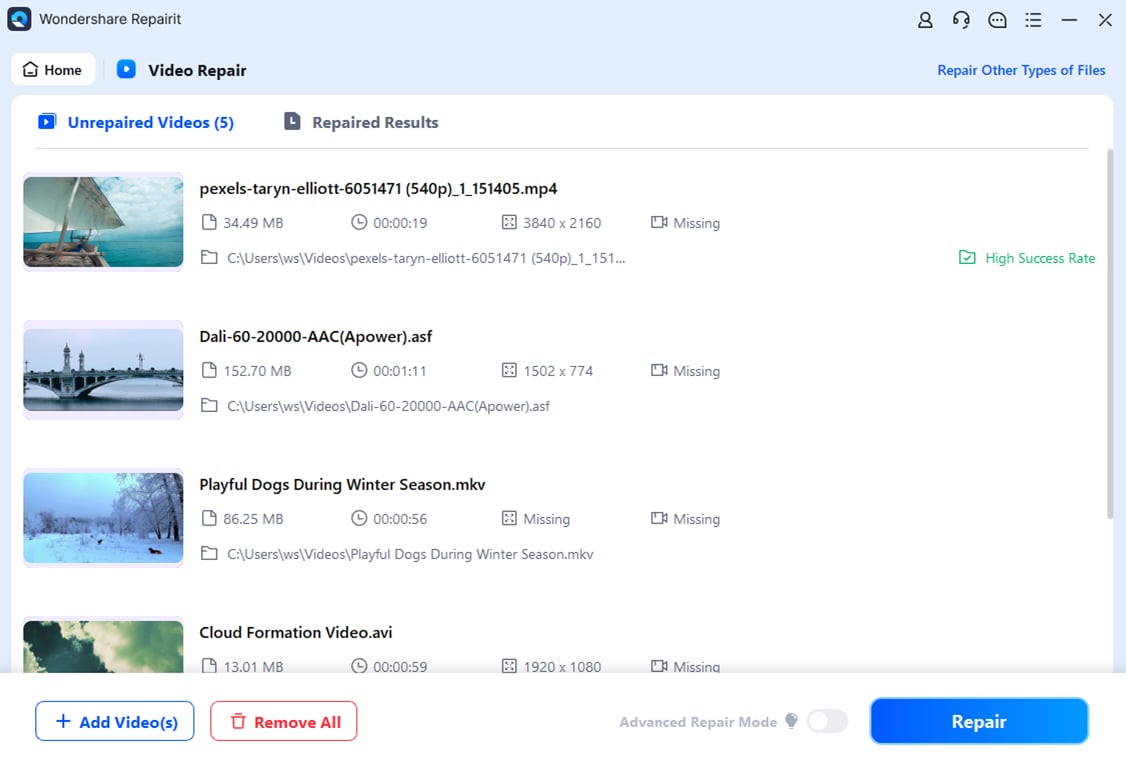
Step 2: Once you've added your corrupted H 26.H 265 videos, the interface will display its Image name, path, size, and more. Click Repair to start the process.
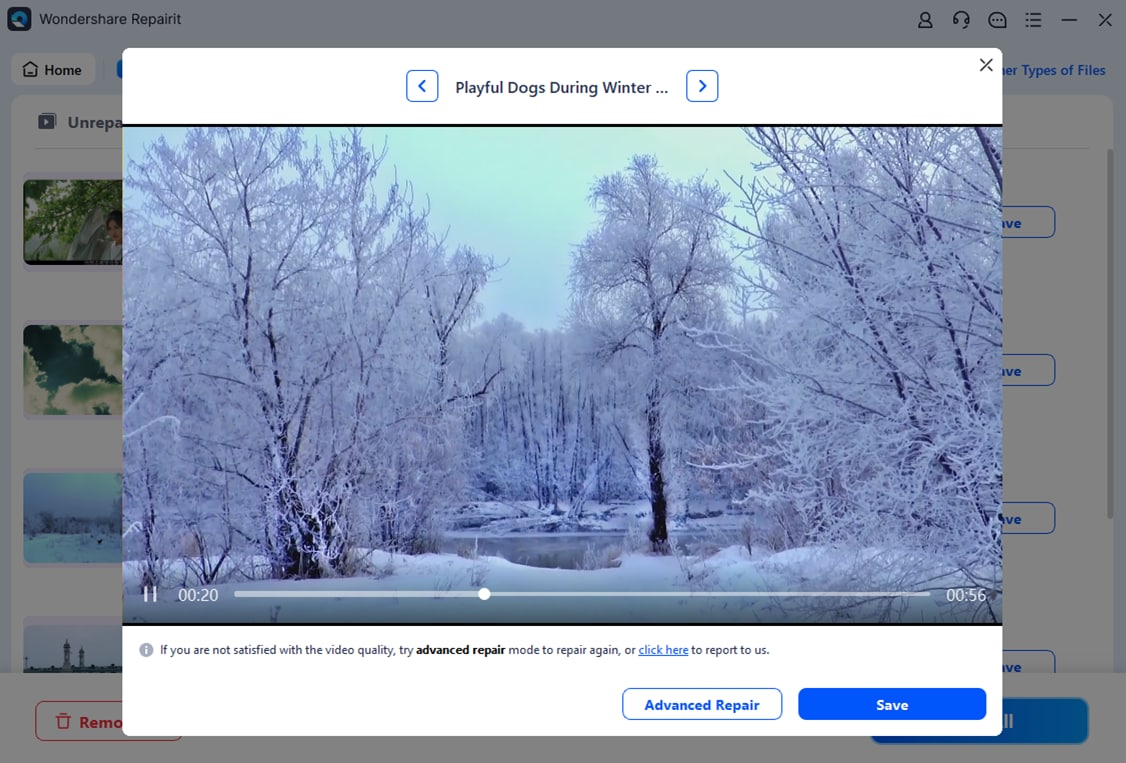
Step 3: Hit Preview to save the repaired H 264.H 265 videos. Ensure they're good to go before saving. If the H 26.H 265 videos look good, click Save to choose where to save them. Do not save them to the same place they were corrupted.
Repair Corrupted H264 and H265 Videos Now

Conclusion
It is important to know the difference between H.264 and H.265 to optimize video quality and efficiency. AVC, or simply H264, is highly compressed with wide compatibility. Hence, it is best suited for streaming over the internet and real-time video communication.
HEVC (H265) compresses files up to 50% smaller while keeping high quality. It supports 4K and 8K resolutions, HDR, and better error concealment for clearer pictures, even on slower connections.
FAQ
-
Are H.264 and H.265 compatible with all devices?
H.264 is more widely compatible with devices and platforms due to its longer presence in the market. H.265 is newer and may not be supported by older devices. However, it is increasingly being adopted by modern devices and platforms. -
Can I convert H.264 video files to H.265?
Yes. Using various video conversion software, you can convert H.264 video files to H.265. This can help minimize file sizes and improve video quality for future playback on compatible devices. -
Which codec is better for live streaming, H.264 or H.265?
H.265 is generally better for live streaming high-quality content due to its superior compression efficiency, which reduces bandwidth usage. However, H.264 is still widely used for live streaming because of its broader compatibility and lower computational demands.


 ChatGPT
ChatGPT
 Perplexity
Perplexity
 Google AI Mode
Google AI Mode
 Grok
Grok