In 2026, when digital operations depend heavily on flawless data transmission, maintaining data integrity is non-negotiable. Similarly, a Cyclic Redundancy Check (CRC) error is not merely a routine system alert; it indicates that the system has detected inconsistencies. Its occurrence signals deeper issues with data corruption or hardware instability, making it essential to understand its significance rather than dismissing it.
With this perspective, keep reading the article to gain a brief understanding of this error, including how it works. In fact, you will be guided on how to recognize this failure on Windows, with signs and symptoms.
Table of Contents
Part 1. Top Reasons for Cyclic Redundancy Check (CRC) Errors on Windows
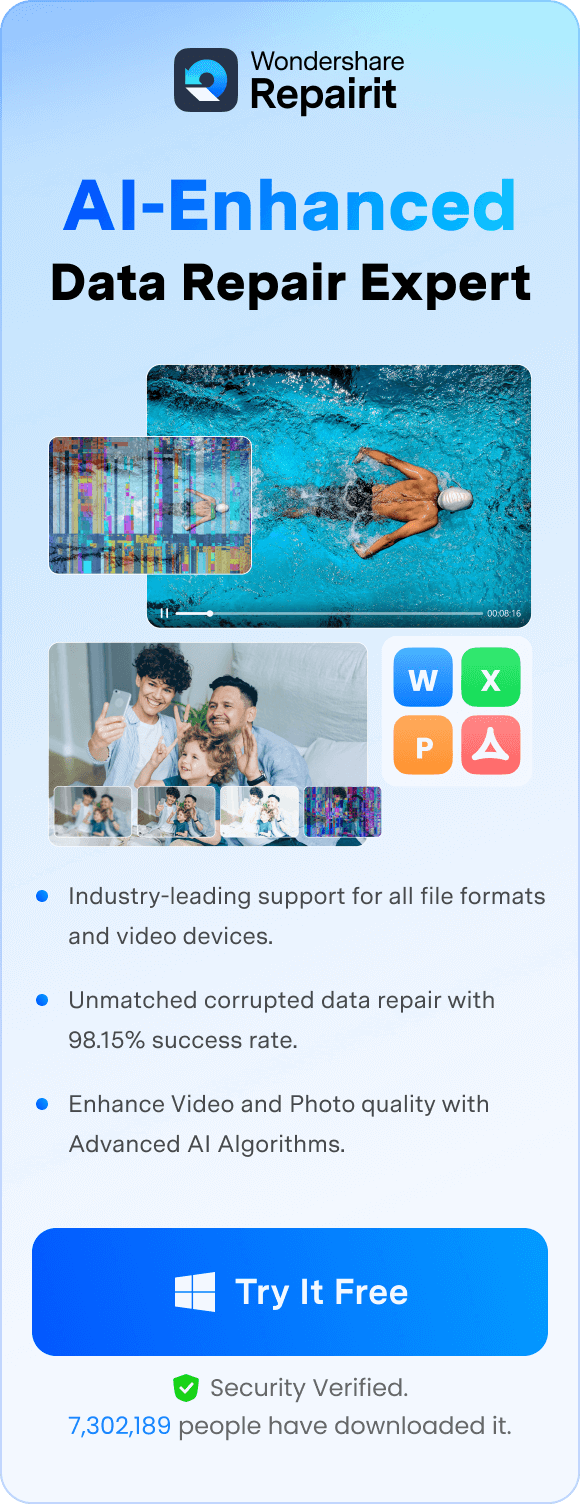
When this verification process fails, it indicates an underlying issue that warrants further investigation. For your assistance, we’ve covered the top reasons behind the Redundancy Checker error, appearing on your Windows:
- Due to Failing Storage Drive: Parts of your hard drive, or SD cards, can get damaged, creating bad sectors where data becomes unreadable. When Windows tries to read data from these spots, the CRC check fails, and you see a data error (CRC).
- Corrupted Files or File System: Even your files can become corrupted if the download is interrupted or a ZIP/archive is damaged. Upon copying or moving such files, the stored CRC value doesn't match the actual data anymore, so Windows reports a CRC error.
- Loose/Damaged Cables or External Enclosures: Worn USB/SATA cables or loose connectors can cause data to be sent with random bit errors. Although your drive is fine, a poor connection can scramble data in transit, causing the CRC test to fail.
- Cluttered or Misconfigured Systems: Failed or partially installed software, registry issues, and misconfigured system files can also trigger access failures during integrity verification. Soon, when Windows attempts to access the damaged data, the integrity check fails, and you receive a CRC error.
- Virus or Buggy Software in Use: Some badly written apps can overwrite or corrupt files while saving, installing, or updating them. Later, when Windows checks those files, the CRC values no longer match, resulting in a CRC error.
Part 2. How CRC Redundancy Checkers Work
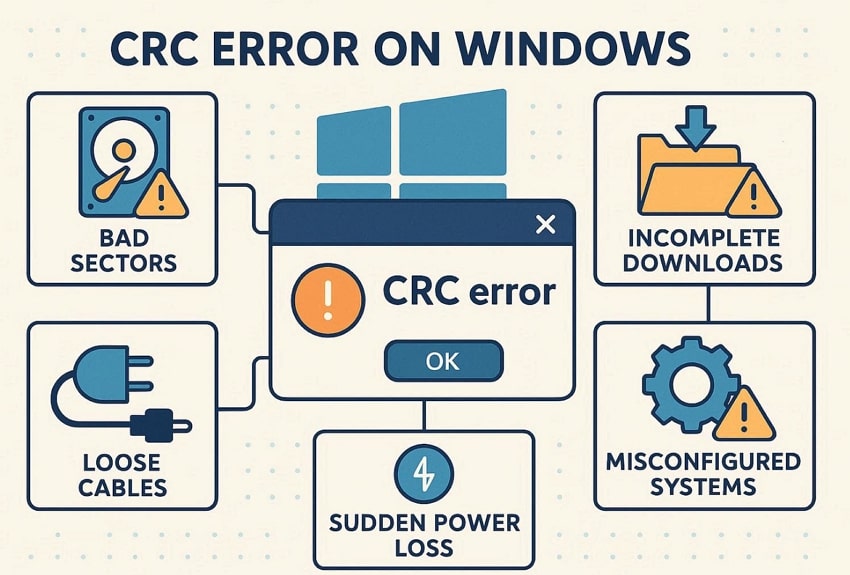
Tools called CRC or disk checkers are used to scan data and drives to determine whether they have been damaged. On Windows, built-in utilities like CHKDSK or vendor disk tools read blocks of data, recalculate CRC values, and compare. As discussed, the Cyclic Redundancy Check verifies data integrity by comparing the stored CRC with the newly calculated CRC. Any mismatch means the data has been changed accidentally and can no longer be trusted.
Difference Between CRC and Other Checksum Methods
Review the provided comparison between CRC and other methods to better understand why CRC is often preferred:
| Aspects | CRC (Cyclic Redundancy Check) | Simple Methods |
| Core Working | Uses polynomial division over binary data to generate a remainder code | Adds byte or word values to generate a total checksum |
| Error Detection Strength | Very strong and detects most random and burst transmission errors | Can miss errors, especially when altered values cancel each other |
| Complexity | Requires polynomial logic and bit-level operations | Very easy to implement and quick to compute |
| Use Cases | Disk storage, USB transfers, network packets, and wireless communications | Basic file checks and low-risk data validation tasks |
Part 3. Recognizing CRC Errors: Signs and Symptoms on Windows
For a timely Cyclic Redundancy Check fix, recognize the following indicators and prevent further data corruption beforehand:

- Data Error (CRC) Pop-Up: When accessing or moving a file/folder, Windows shows a CRC message and cancels the action. This is the clearest sign that Windows attempted to verify the data and found it did not match expectations.
- File or Disk is Not Accessible Messages: You might face errors like “D:\ is not accessible.”, or data error (CRC) for an external drive or partition. This means the drive/folder appears in File Explorer, but Windows refuses to open it because the integrity check failed.
- Copy or Extraction Stops Partway Through: Copying files or unzipping an archive starts normally, then suddenly stops with an error such as CRC failed. Users might end up with some files copied or a partially extracted folder that will not open later.
- Some Files Open but Look Corrupted: A document or image might open but show missing pages or a blank section, or videos end unexpectedly. This often means the program failed to read damaged sectors after Windows reported a read error.
- Slow Access or Hangs When Opening Files: Double‑clicking a file on a problem drive makes Explorer or the app hang for a long time before showing an error. The delay occurs because Windows repeatedly attempts to read bad sectors, then finally gives up and logs a CRC error.
Part 4. 7 Proven Methods to Repair CRC Errors on Windows PCs
Once you notice the early signs and symptoms of a Cyclic Redundancy Check (CRC) error, addressing it promptly becomes more important. With that in mind, the section covers 7 tried and tested methods to fix this error on your Windows:
1. Stop Using the Affected Drive
Every read/write operation on a compromised drive increases the risk of overwriting or further damaging existing data. Consider ceasing use, as it reduces the risk of further escalation and gives any recovery tool a better chance of retrieving intact files. Plus, use the drive only for diagnostic or recovery purposes until the issue is resolved.
2. Back Up What Is Still Readable
Even if a drive is partially corrupted, some files may still be intact and readable. Thus, copy off or back up any important files that are still open without errors from the affected drive. Also, prioritize key folders and skip any files that immediately activate the CRC check error. This precaution reduces the risk of complete loss and allows you to continue working without fear.

3. Check Cables, Ports, and Re‑download Files
Simple, fixable issues, such as loose or damaged cables or corrupted downloads, cause many CRC errors. In this context, inspecting connections and re-downloading files, when necessary, often resolves the error without complex repairs. Simply, try connecting the drive to a different port or another computer to rule out a port-specific issue. If it still appears on downloaded files, re-download them from a trusted source to ensure file integrity.
4. Run CHKDSK Carefully
Windows built-in disk-checking tool, CHKDSK, helps detect and repair file system errors or bad sectors instantly. Essentially, it recovers inaccessible data, corrects file allocation issues, and even restores the drive’s reliability. Dive into the tutorial to run a comprehensive scan and fix data error Cyclic Redundancy Check on Windows:
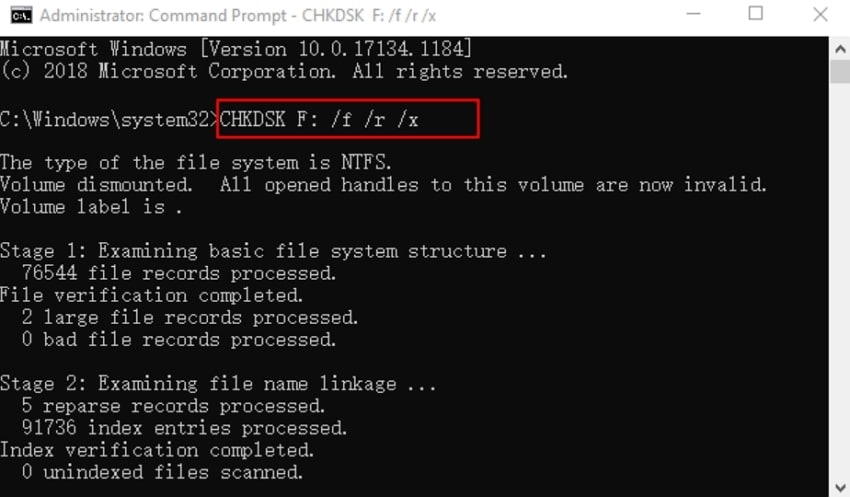
Step 1. Initially, type “cmd” in the search box for Windows and run Command Prompt as an Administrator.
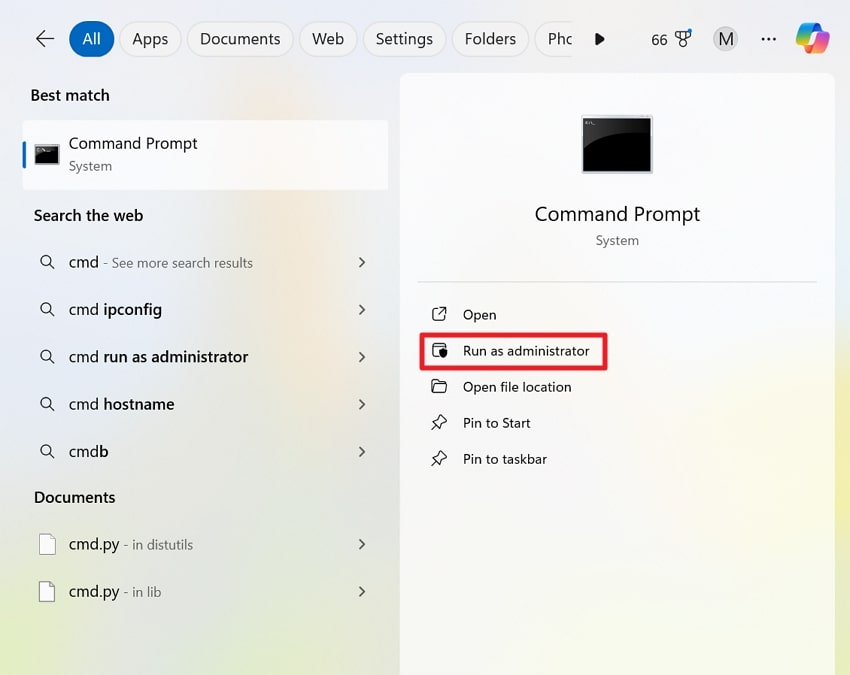
Step 2. Now, write “chkdsk F: /f /r /x” in Diskpart and press Enter to start the repair of file-system errors. Following this, replace “F:” with the drive letter of your hard drive with the Cyclic Redundancy Check error.
5. Repair System Files (When CRC Appears in Windows Operations)
CRC errors can sometimes occur not because of the drive itself, but due to corrupted or missing system files. A complete repair of such files ensures that CRC-check errors caused by software-level issues are resolved, restoring normal system operations. This approach is valuable when a CRC error occurs during routine Windows tasks such as copying files. Follow the guidelines to understand how to repair system files and prevent such errors later:
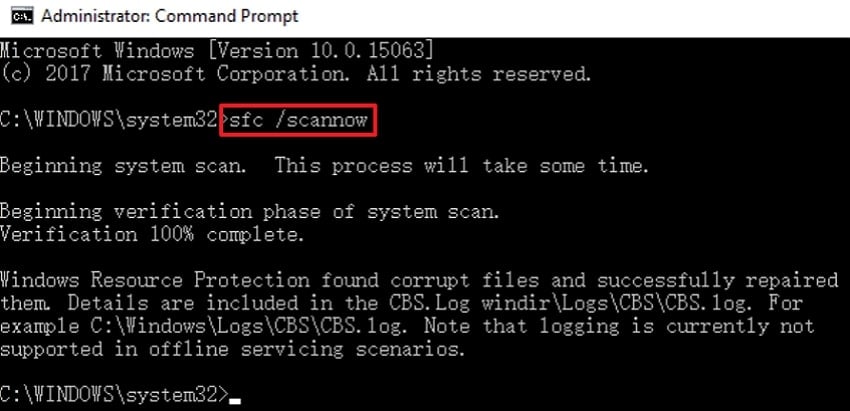
Instructions: Run Command Prompt as an administrator, then type “DISM.exe /Online /Cleanup-image /Restorehealth” and hit the Enter key. Once the DISM command completes, write “sfc /scannow” in the elevated prompt window to process repair. When the repair is finished, restart your computer and reopen the device to use the saved data.
6. Recover Data Before Formatting or Reinitializing
When your drive shows a CRC error, and Windows says you need to format it, never format it right away. Formatting can make recovery much harder, or even impossible, because it rewrites how data is stored on disk. Instead, use a data recovery software like Recoverit that can read from damaged, RAW, and unreadable files. More impressively, it scans problematic drives and finds deleted or corrupted files, videos, or images.
The program supports over 1000 lost scenarios, including accidental deletion, system crashes, and formatting. Essentially, you get 100% secure recovery and support for more than 1,000 file formats. Notably, it's a leading data recovery platform with a 99.5% success rate and a 5-minute average scan time.
7. Repair CRC‑damaged Archives or Media Files
For a damaged ZIP/RAR archive or a document that shows a Cyclic Redundancy Check error, a repair tool is often needed. The program, Repairit, is built for this; it can repair many types of corrupted files while keeping the original layout. It handles CRC-related corruption in archives and other files, restoring the internal structure to its integrity. Importantly, you can even restore compressed contents from your documents, images, and more.
It supports both standard and multi-volume RAR files, whether created by WinRAR or other compression tools. Users can fix ZIP files and files larger than 1G at the same time for immediate repair. With preview support, you can easily review the internal hierarchy before downloading the final version. Additionally, it preserves the layout, tables, and design elements in your iWork files, displaying a CRC check error upon access.
Key Features

-
Repair Engineering Files: The program repairs PSD, CAD, and other complex project files, rebuilding layers, metadata, and previews.
-
Fixes Excel Documents: You can restore corrupted formulas, charts, and content in the damaged Excel files within seconds.
-
Complete Compatibility and System Support: It supports all versions of Microsoft Office and Adobe files with no feature loss across platforms.
Simple Step-by-Step Tutorial to Repair CRC‑damaged Archives via Repairit
Follow the structured guidelines and repair damaged archives for a reliable Cyclic Redundancy Check fix:
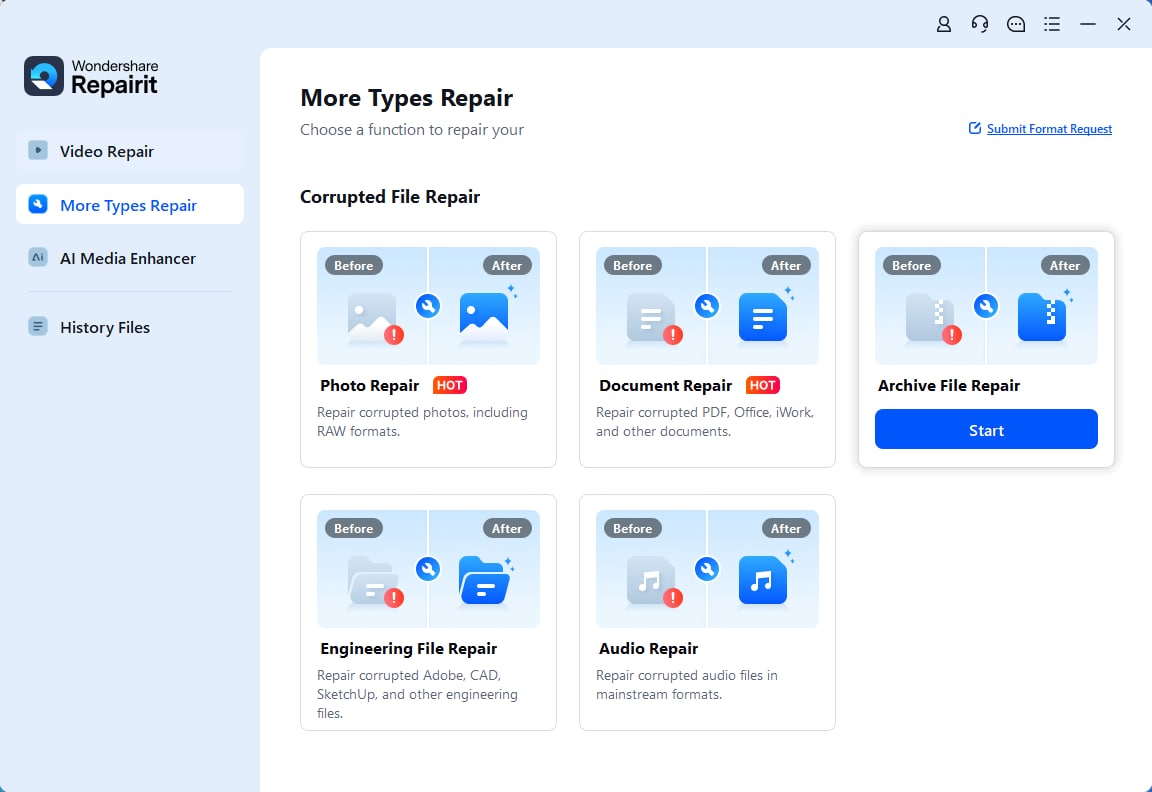
Step 1. Access the Archive File Repair Tool
To do so, access the “More Types Repair” toolkit and click the “Start” button for Archive File Repair.
Step 2. Incorporated CRC-Damaged Archives into the Tool
Later, press the “+Add” button to add all the corrupted archives for a complete repair.
Step 3. Initiate the Process of Archive Repair
Once done, navigate to the “Repair” button and get your corrupted files repaired immediately. Finally, preview the files after repair and save them on your device for later use.
Repair CRC‑damaged Archives via Repairit Now

Conclusion
In summary, a Cyclic Redundancy Check (CRC) error serves as a vital warning that data integrity has been compromised for any possible reason. As the article explains, understanding the causes, recognizing early signs, and applying appropriate repair strategies are essential to protecting valuable data. Also, if CRC errors specifically affect compressed or archived files, only Repairit is recommended as a reliable repair solution.
Frequently Asked Questions
-
1. Can CRC errors occur on SSDs, or only on hard drives?
Indeed, the CRC-check errors can occur on both SSDs and your traditional hard drives. While SSDs do not have physical bad sectors like HDDs, CRC errors on SSDs might result from firmware issues or connection problems. -
2. Is it safe to ignore a CRC error if the file seems to open normally?
Ignoring a CRC error is never recommended, even if the file appears to open and function normally at first. This error indicates underlying data inconsistencies that may not be immediately visible but can progressively degrade the file’s integrity. What seems usable today may become unreadable later, especially when the file is edited, transferred, or compressed again. -
3. Are CRC errors related to file size?
Larger files are more prone to CRC errors because they contain more data segments, increasing the chance of corruption during transfer. Even a brief read/write failure can affect part of a large file, triggering a CRC error when the system attempts to verify.


 ChatGPT
ChatGPT
 Perplexity
Perplexity
 Google AI Mode
Google AI Mode
 Grok
Grok