“What are RAW files?”
If you've worked with a video production company, you might have heard the term "RAW video files". You might not fully understand what this means if you're not in the video production field. To clarify, we'll explain the RAW video file format and how it’s open for production.
In this article
Part 1. What Is RAW Video Format?
RAW files, short for "Raw Audiovisual Workflow," are often referred to as "source footage" in video production. These files capture the purest form of footage directly from the camera sensor – retaining all the original data without any compression or processing. This makes them highly flexible for post-production editing, similar to a digital equivalent of a film negative.
Unlike ready-to-use formats like MP4, RAW files are not immediately viewable or usable. They lack enhancements such as color correction, audio improvements, and editing, requiring significant post-production work. This is why they might appear flat, disorganized, and lifeless initially.
RAW files capture every detail of a scene in its unaltered state. This provides maximum creative control during post-production. They preserve original color data and light intensity, allowing editors to make precise adjustments for color grading. This enhances the visual and emotional impact of the video. These are ideal for projects with extensive visual effects.
Part 2. RAW Video VS Standard Video

Standard video formats undergo significant camera processing. They introduce different video elements and reduce quality to prioritize smaller file sizes. In contrast, RAW video file format preserves the full dynamic range in raw shots.
Shooting in RAW format offers unmatched flexibility in editing – from exposure and white balance adjustments to intricate color grading and sharpness tweaks. However, a large storage is required for storing videos.
| Feature | RAW Video | Standard Video |
| Image Quality | Highest possible, with no loss of details | Lower due to compression and processing |
| Post-production Flexibility | Extensive control and manipulation | Limited by loss of data and compression |
| File Size | Large, requiring more storage | Smaller, more manageable for casual use |
| Suitable Applications | Professional production with high-quality output | General use, casual videography, quick sharing |
Part 3. How to Easily Repair RAW Video Format?
Storing RAW videos can be stressful and complicated due to their large size and the need for proper organization. Losing files can render footage unusable. Many individuals or smaller organizations lack professionals to manage and share footage, leading to mistakes and accidental deletions. To avoid this, use video repair software like Repairit RAW Video Repair.
Repairit easily repairs RAW video files on Windows and Mac within seconds. It has a simple user interface so all user levels can utilize it. Here are its other features:

-
Works with RAW and all popular video formats (AVI, MOV, MKV, MP4, etc.) and recovers Full HD, Ultra HD, 4K, and 8K videos without corruption.
-
Repairs RAW footage from professional cameras, memory cards, computers, external drives, NAS storage, or USB flash drives.
-
Fixes videos lost due to disk formatting, power outages, malware attacks, accidental deletion, damage, etc.
-
Repairit has an Advanced Video Repair feature for you to expertly repair RAW videos.
-
Repairit has a quick and advanced scanning mode. You can use either depending on the level of corruption the video file has undergone.
-
No limit to the number and size of the repairable videos.
-
Support Windows 11/10/8/7/Vista, Windows Server 2003/2008/2012/2016/2019/2022, and macOS 10.10~macOS 13.
Follow these steps to repair RAW videos using Repairit:
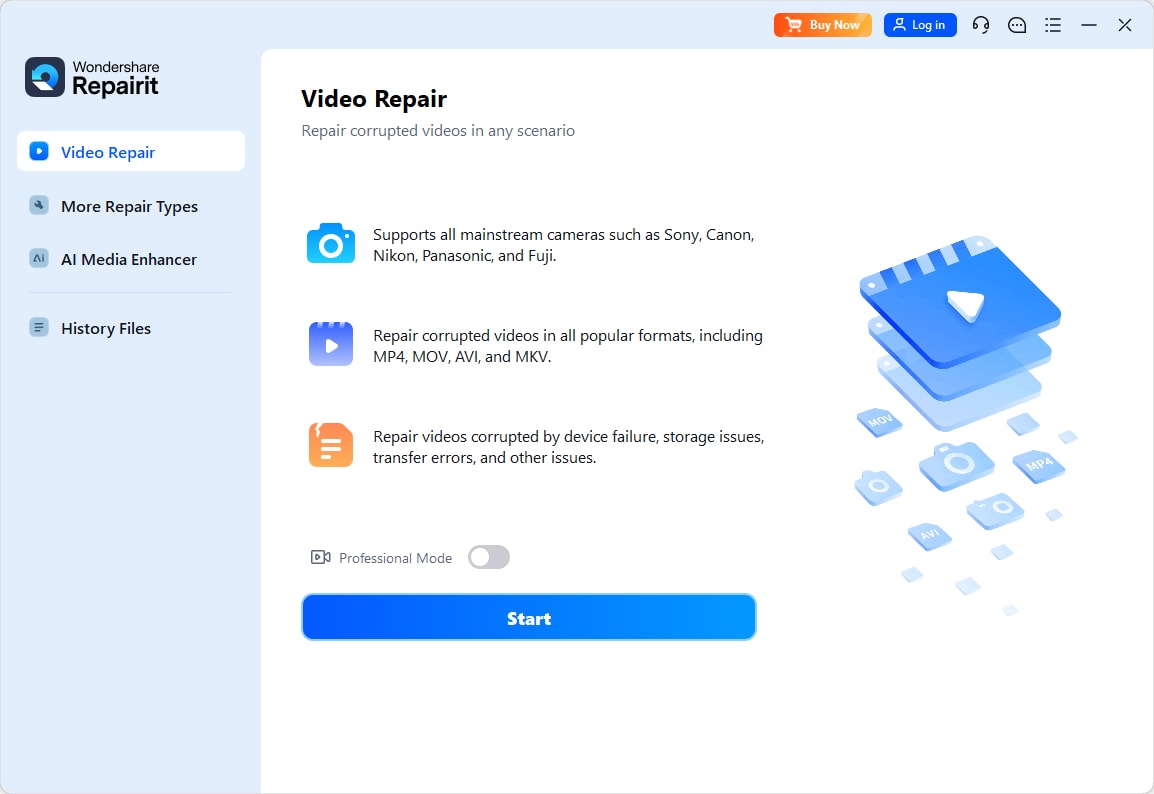
Step 1: Download and open the Repairit RAW Video Repair tool. Click the Add button to start repairing.
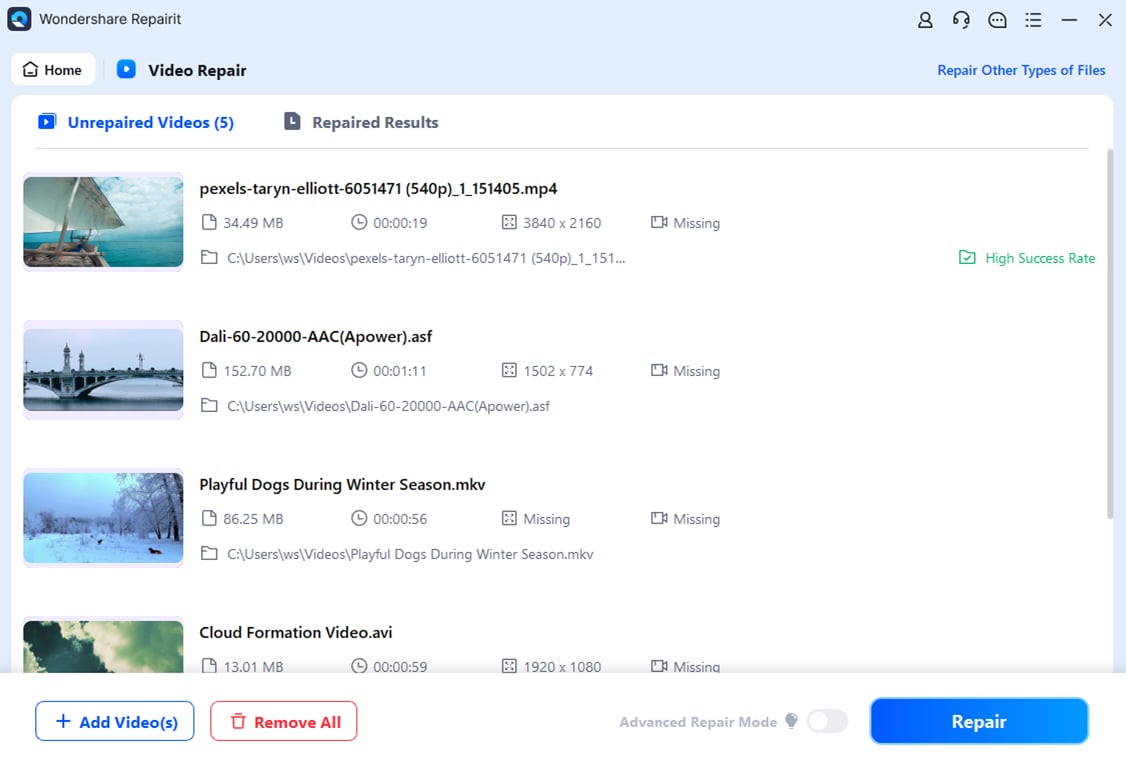
Step 2: View RAW video details (Image name, Path, Size, Watching Time, Resolution, Equipment). Click Repair to start repairing.
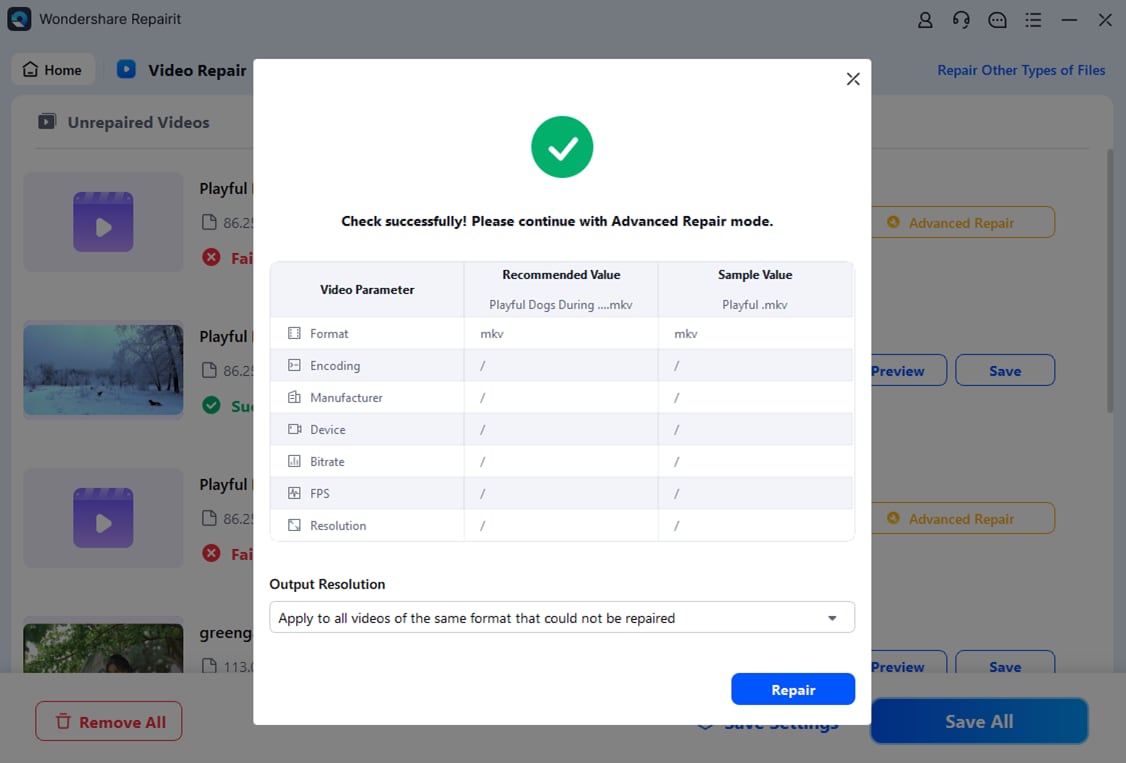
Step 3: Double-click to preview the repaired RAW videos. You can also click Preview to check the videos. If satisfied, click Save and choose a different path from the original location.
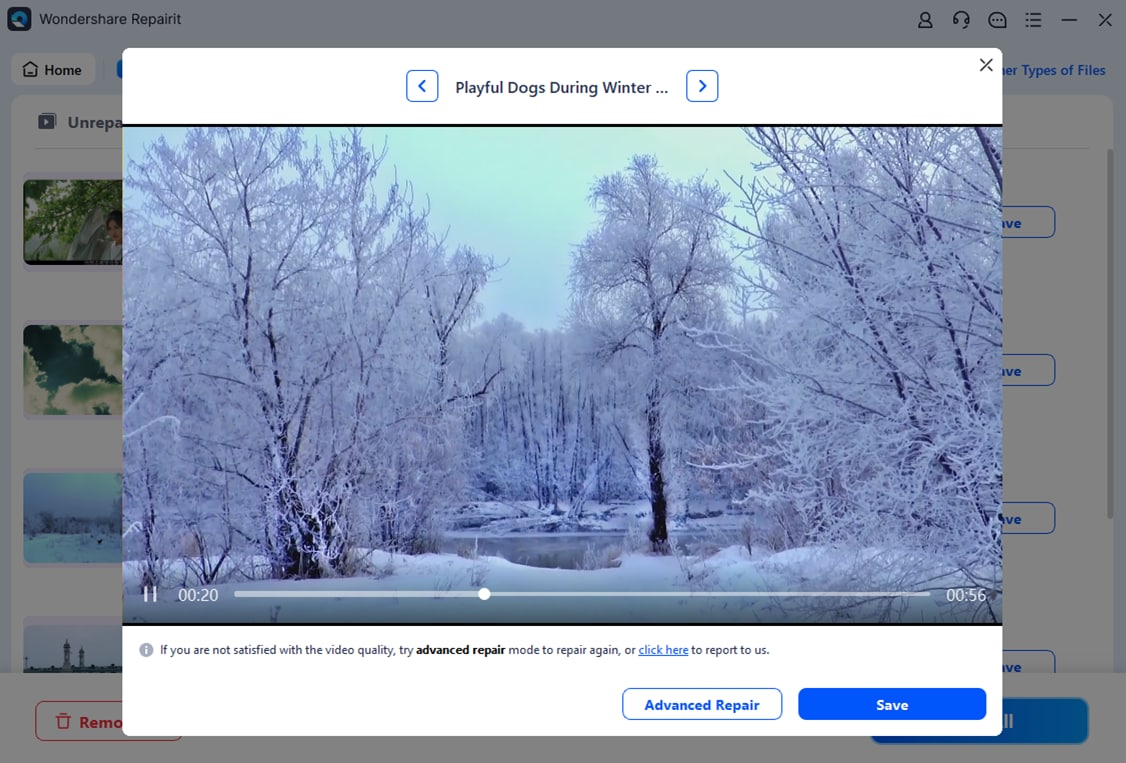
Easily Repair RAW Video Format with Repairit Now

Part 4. How to Open RAW Video Files?
You need editing software like Adobe Photoshop or Lightroom to open a RAW file. The best software depends on your camera type and operating system. Once opened, you can convert and export the RAW file to your desired format.
Here are the quick steps to open RAW files using Lightroom:
Step 1: Link your camera or external drive to your computer.
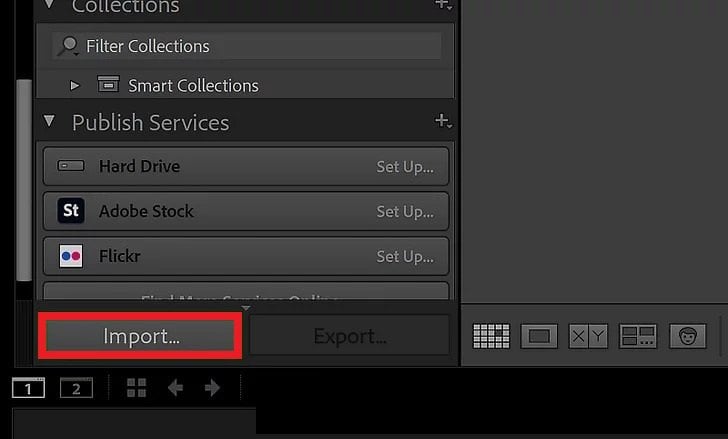
Step 2: Open the Lightroom. Press Import, located in the lower-left corner.\
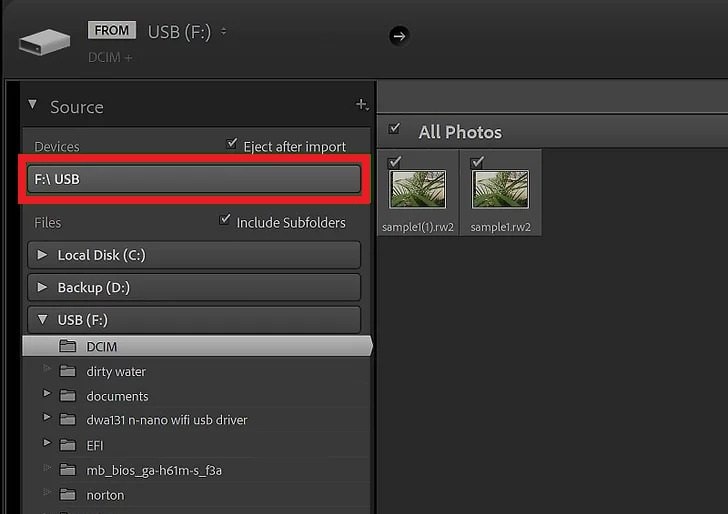
Step 3: Select your camera or card reader. Find it in the menu bar on the left under Source.
Step 4: Double-click the RAW file to open it.
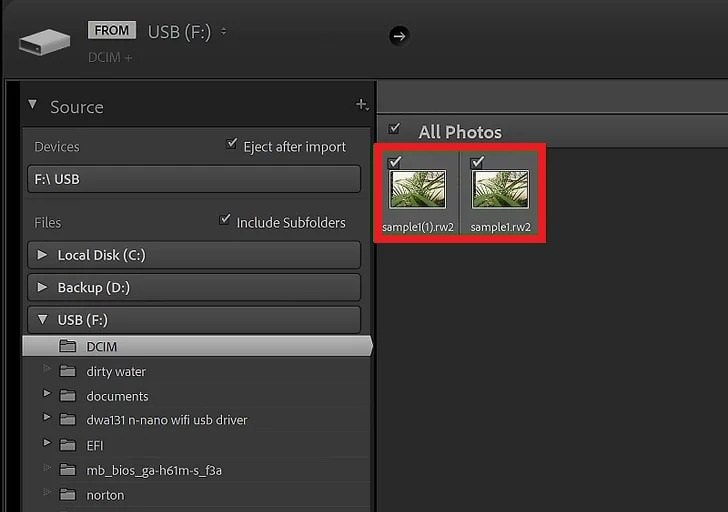
Step 5: To copy or move files to your computer, check the box in the upper-right corner of the image preview and click Copy or Move at the top of the page.
Part 5. What’s the Difference Between Sony Raw Video and Canon?
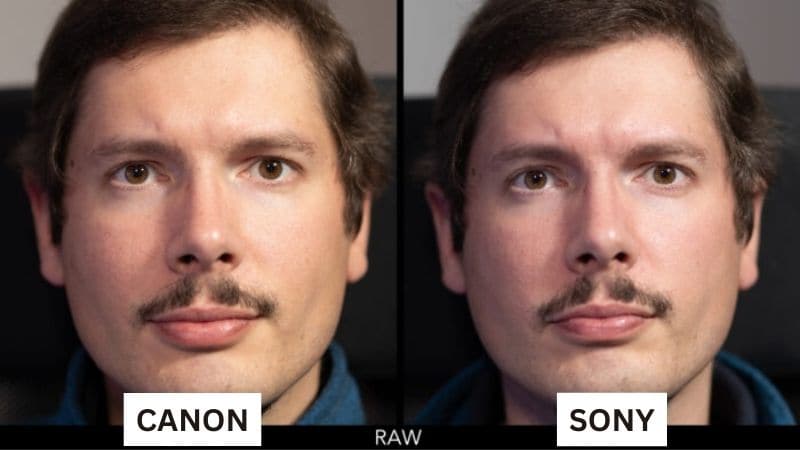

Sony has been known for their innovative and high-quality imaging technology. Sony RAW video format, used in high-end cameras like the FX6, FX9, and Alpha series, offers uncompressed and lossless footage. This format is valued for retaining all sensor data for post-production. Sony RAW is favored for its dynamic range, color depth, and control during color grading and editing.
On the other hand, Canon is another industry leader renowned for its contributions to still photography and video production. Canon RAW video format, featured in the Cinema EOS and EOS R series, offers similar benefits in image quality and post-production flexibility. Known for its rich color science, Canon RAW provides uncompressed videos with high detail and dynamic range.
| Feature | Sony RAW Video Format | Canon RAW Video Format |
| Camera Series | FX6, FX9, Alpha series | Cinema EOS series, EOS R series |
| Dynamic Range | High, offering extensive post-production control | High, known for excellent highlight recovery |
| Color Science | Accurate and versatile | Renowned for rich and pleasing colors |
| File Compression | Typically uncompressed or lightly compressed | Uncompressed or lightly compressed |
| Bit Depth | Up to 16-bit | Up to 12-bit or 14-bit, depending on the model |
| Recording Formats | RAW, X-OCN (extended), and others | Cinema RAW Light, RAW |
| Usage | Suitable for practical video applications | Favored for cinematic and high-quality productions |
| Low Light Performance | Excellent, especially in Alpha series | Excellent, especially in the Cinema EOS series |
Conclusion
The RAW video format offers exceptional flexibility and control in post-production, which is ideal for professional projects. Unlike compressed standard video formats, RAW captures unaltered details. Thus preserving maximum quality and dynamic range. Despite larger file sizes and the need for software like Lightroom, RAW's advantages in color grading and visual effects are significant.
FAQ
-
How do I edit RAW video files?
Editing RAW video files requires specialized software that can handle the uncompressed data. Popular options are DaVinci Resolve and Final Cut Pro. These programs allow you to work with high-quality footage and perform color grading, noise reduction, and other advanced edits. -
Do I need a special computer to work with RAW video files?
Working with RAW video files requires a computer with a powerful processor, ample RAM, and a fast storage solution (like SSD) to handle the large file sizes and intensive processing demands. A dedicated graphics card (GPU) can also significantly improve performance during editing and rendering. -
How do I ensure the best quality when working with RAW video files?
To maintain the best quality, avoid unnecessary conversions and transcoding, use high-quality lenses and camera settings, and ensure proper lighting during shooting. Use professional-grade software and color grading techniques in post-production to maximize the footage's potential.

 ChatGPT
ChatGPT
 Perplexity
Perplexity
 Google AI Mode
Google AI Mode
 Grok
Grok