Excel is a powerful tool for handling data. But, sometimes you may find your file is too big to open, slows down to a crawl, or even crashes the program. Why does this happen? Often it comes down to formatting bloat, complex formulas, images, or even file corruption. The good news is you don’t need to give up on your spreadsheet.
In this guide, you will learn why “Excel files become too big” problem happens. You will also discover 8 ways to reduce Excel file size.
Table of Contents
-
- Fix 1. Remove Unnecessary Formatting & Styles
- Fix 2. Delete Unused Rows, Columns & Worksheets
- Fix 3. Compress Images or Replace with Links
- Fix 4. Simplify Formulas & Limit Pivot Tables
- Fix 5. Save in Modern Formats (.xlsx)
- Fix 6. Use Power Query or Database Integration for Large Data
- Fix 7. Split Data Across Multiple Files
- Fix 8. Enable Compression in Windows/Cloud Storage
Part 1: Problems Caused by Oversized Excel Files
When an Excel file becomes too big to open, the effects can show up in more ways than just slow performance. Here are the most common huge Excel file problems you may run into:
- Lag and freezing. The file takes longer to respond, making basic tasks like scrolling or typing frustratingly slow. Over time, this slows down your entire workflow.
- Crashes and instability. Large files push Excel beyond its limits, leading to unexpected shutdowns. This can cost you hours of unsaved work.
- Error messages. You may see alerts like “Excel file too large to open,” which block access completely until the issue is fixed.
- Sharing issues. Oversized files are often too big for email attachments and can take forever to upload to cloud platforms, making collaboration harder.
- Higher chance of corruption. The larger and heavier the file, the more likely it is to become corrupted, especially if Excel crashes mid-use.
Part 2: Why Excel Files Become Too Large
Oversized files don’t just happen out of nowhere. They usually grow over time as more data and formatting are added. Some of the main causes include:
- Excessive formatting. Using too many styles, colors, or merged cells bloats the file, even if it looks simple on the surface.
- Unused rows and columns. Hidden or empty-looking cells may still hold formatting or data, and Excel treats them as part of the file.
- Images and objects. Inserting multiple high-resolution pictures, shapes, or charts quickly increases file size.
- Complex formulas and pivot tables. Heavy calculations or multiple pivot tables increase both file weight and the time Excel needs to process data.
- External links or embedded data. Linking to other files or embedding large datasets can silently add bulk, making the file harder to manage.
Part 3: How to Reduce Excel File Size (Step-by-Step)
Now that you know what makes Excel files too large, let’s look at practical ways to reduce their size. Each fix tackles a different cause, and using them together can make a big difference.
Fix 1. Remove Unnecessary Formatting & Styles
Formatting Excel files seems harmless. But, when you overdone it, it adds invisible weight. Cleaning up extra styles or color fills can help Excel run faster and keep the file smaller.
Step 1. Open your Excel file.
Step 2. Select the entire worksheet. You can press Ctrl + A.
Step 3. Go to the Home tab and click Clear. Select Clear Formats.
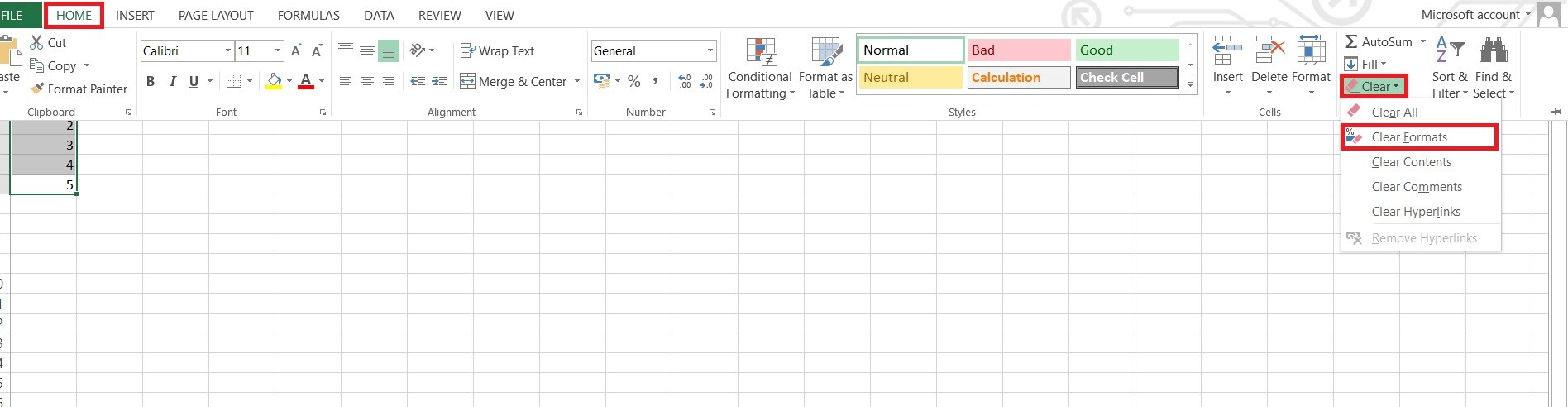
Step 4. Reapply only the essential formatting you actually need.
Fix 2. Delete Unused Rows, Columns & Worksheets
Does your spreadsheet have large empty areas that were once formatted? They still take up space. Removing these extra rows, columns, or even entire unused sheets can instantly shrink the file size.
Step 1. Highlight any empty rows or columns at the bottom and right side of your data.
Step 2. Right-click and choose Delete to remove them completely.
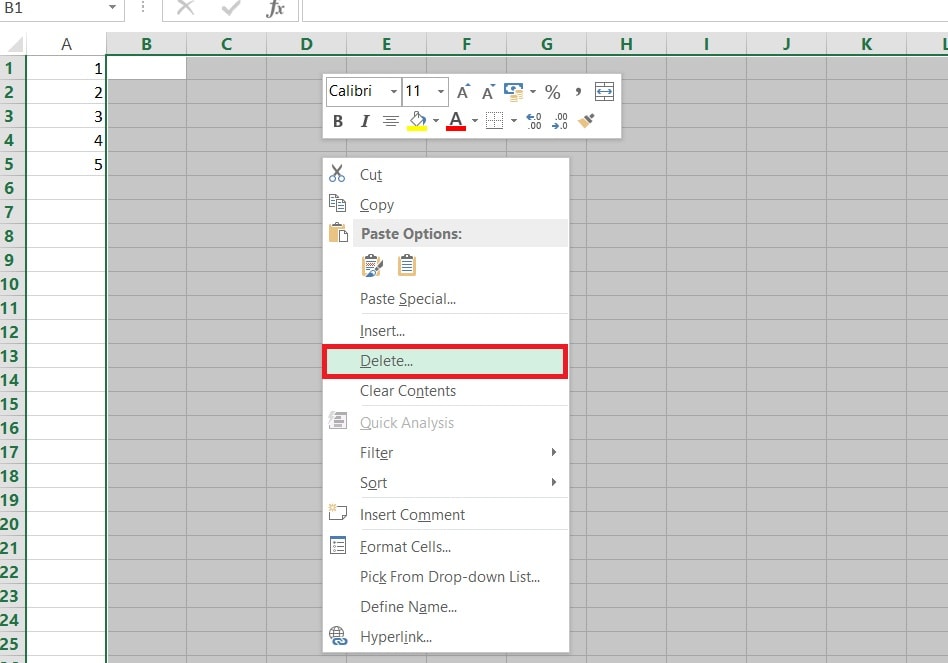
Step 3. If there are extra worksheets you don’t use, right-click their tabs and select Delete.
Fix 3. Compress Images or Replace with Links
High-resolution images take up a lot of space inside Excel. Compress them or use links to external files instead. This way you can reduce size without losing the visuals you need.
Step 1. Click on an image inside your Excel file.
Step 2. Go to the Picture Format tab and select Compress Pictures.
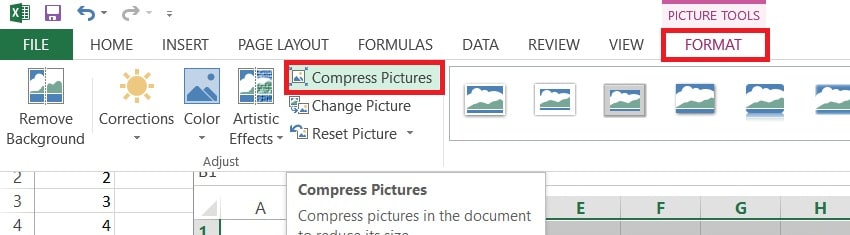
Step 3. Choose a lower resolution or apply compression to all images in the file. Alternatively, replace images by inserting hyperlinks to external files instead.
Fix 4. Simplify Formulas & Limit Pivot Tables
Complex formulas and multiple pivot tables may seem necessary, but they can often be streamlined. Simplifying calculations or reducing duplicate pivot tables not only saves space. It also speeds up performance.
Step 1. Look for repeated formulas and replace them with static values if the numbers won’t change.
Step 2. Use simpler functions instead of complex nested ones where possible.
Step 3. Combine multiple pivot tables into a single one if they use the same dataset.
Fix 5. Save in Modern Formats (.xlsx)
Older Excel formats like .xls store data less efficiently. Saving your file in the .xlsx format compresses the content automatically. This often cuts the size down significantly.
Step 1. Go to File.
Step 2. Click Save As and choose a destination folder.
Step 3. From the dropdown menu, select Excel Workbook (*.xlsx).
Step 4. Save the file and compare the new size with the original.
Fix 6. Use Power Query or Database Integration for Large Data
If you’re handling very large datasets, Excel may not be the best place to store all the raw information. Using Power Query or connecting to a database can keep the main file lighter. You can do this while still letting you analyze large amounts of data.
Step 1. Open a new Excel file.
Step 2. Go to DATA.
Step 3. Click Get Data and choose From File or From Database.
Step 4. Connect to your source (CSV, SQL database, etc.).
Step 5. Load only the data you need into Excel instead of importing everything.
Fix 7. Split Data Across Multiple Files
Sometimes the simplest solution is breaking a too big spreadsheet into smaller, manageable parts. This makes each file easier to open and reduces the risk of crashes.
Step 1. Open your large file and decide on logical sections. It could be by year, project, or department.
Step 2. Copy each section into a new Excel file.
Step 3. Save each smaller file separately and keep them organized in one folder.
Fix 8. Enable Compression in Windows/Cloud Storage
Beyond Excel itself, you can use file compression features built into Windows or cloud platforms. This won’t change the content of your file. However, this makes it lighter to store and share.
Steps (Windows):
Step 1. Right-click on your Excel file.
Step 2. Select Compress to and choose from ZIP, 7z, TAR, etc.
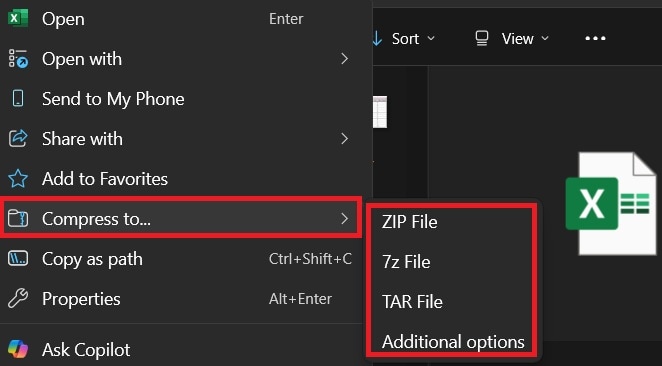
Step 3. A smaller ZIP version of the file will appear in the same location.
Steps (Cloud):
Step 1. Upload your file to OneDrive, Google Drive, or Dropbox.
Step 2. Enable their built-in compression or sharing optimization features.
Part 4: What If Your Excel File Is Too Big and Won’t Open?
Sometimes, the issue goes beyond size. A file that’s too large can become corrupted, making it impossible to open no matter how many times you try. This can be frustrating if the file contains important data you can’t afford to lose.
When this happens, a specialized repair tool is the safest way forward. One reliable option is Repairit Excel File Repair.
Key Features of Repairit Excel File Repair
- Repairs corrupted or oversized Excel files that fail to open.
- Supports both .xls and .xlsx formats.
- Recovers all elements, including formulas, tables, charts, and cell formatting.
- Works on files that are too big, too slow, or stuck in error loops.
- User-friendly design, so you don’t need advanced technical skills.
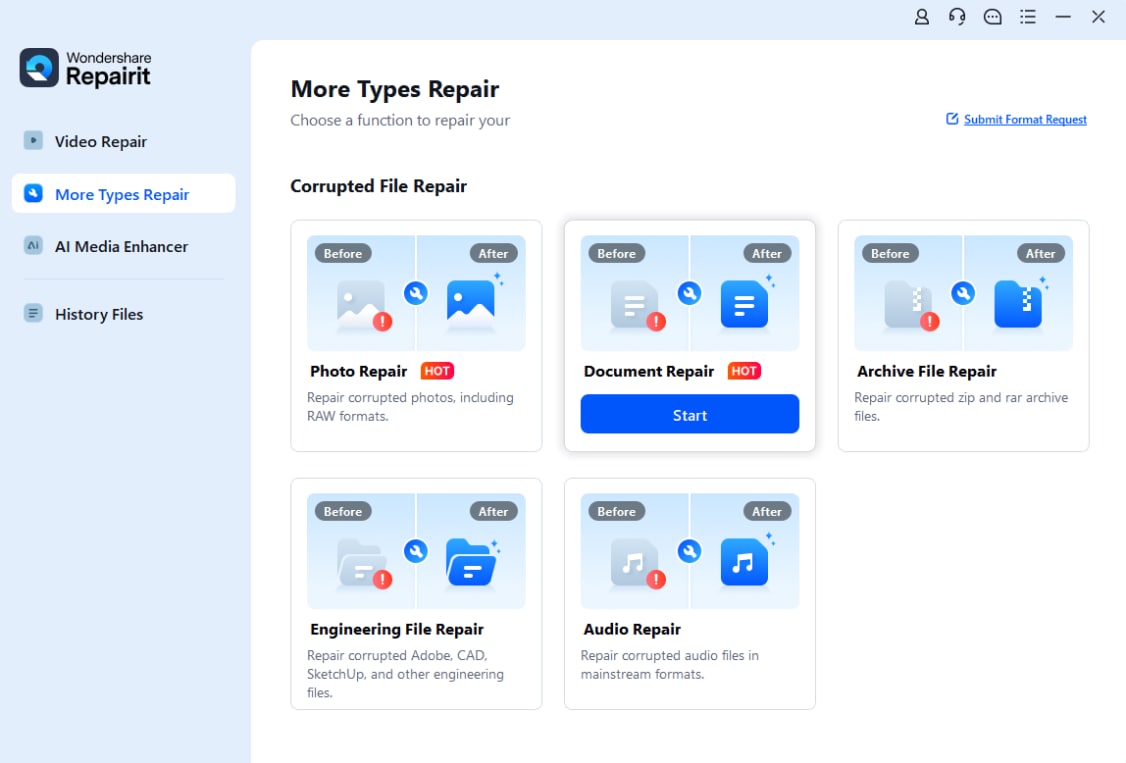
Step 1. Open Repairit on your computer and select Document Repair.
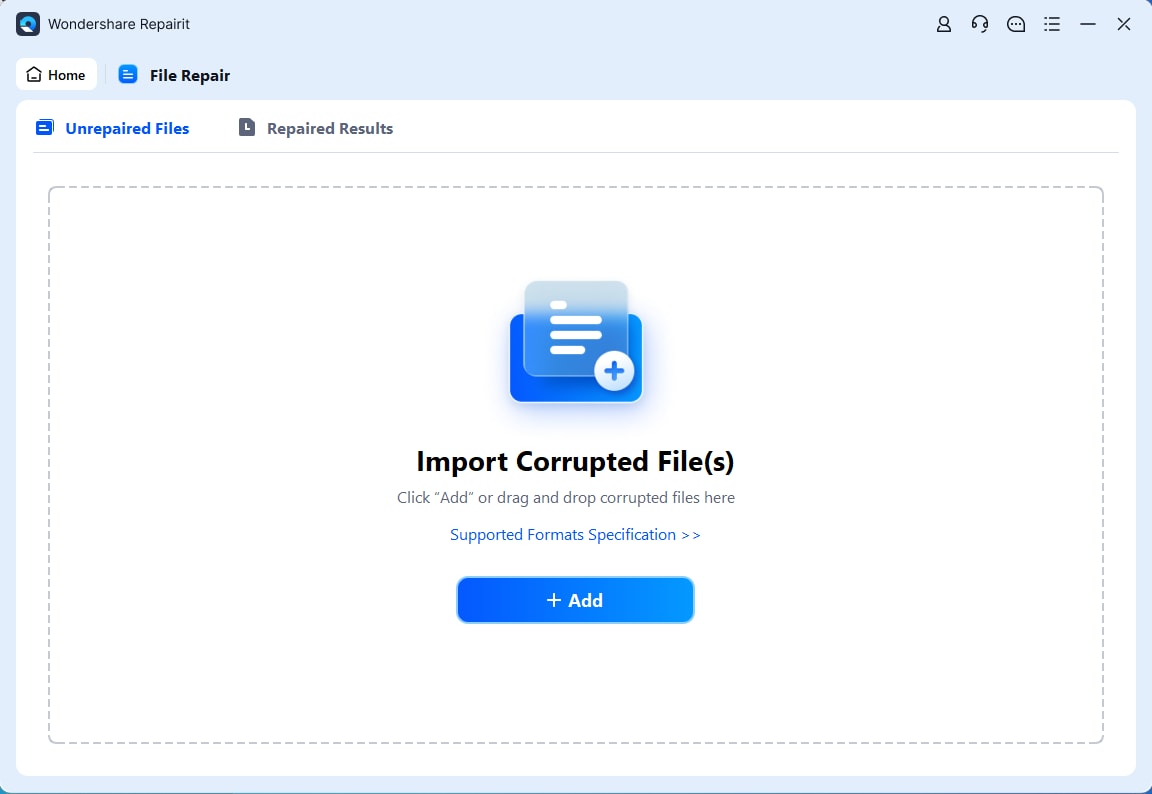
Step 2. Click +Add and choose your Excel files that won’t open.
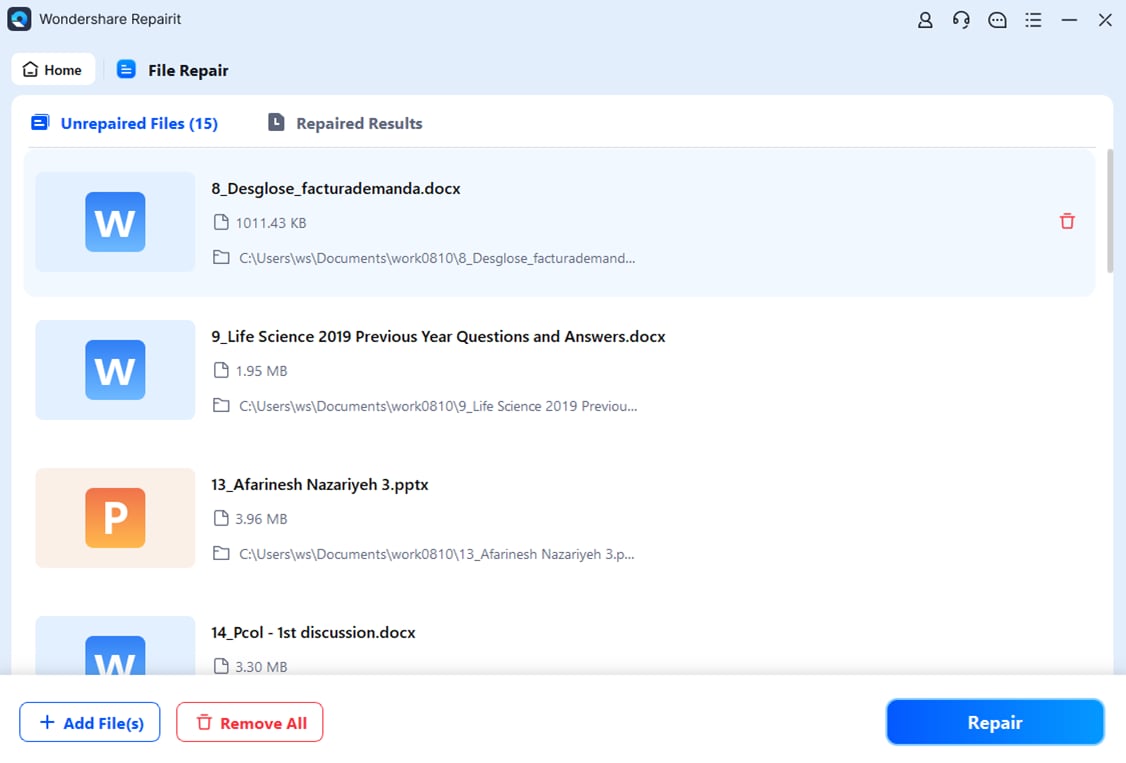
Step 3. Hit Repair.
Step 4. Once the repair finishes, preview the Excel files. If you are satisfied, Save them in a safe location.
Part 5: Extra Tips to Prevent Oversized Excel Files
Fixing a large file is one thing, but wouldn’t it be easier to stop them from getting that big in the first place? Here are some habits to keep your spreadsheets under control:
- Use .xlsx format by default. It’s designed to be more efficient and compresses data automatically, which keeps file sizes smaller.
- Clean up regularly. Removing old formatting, unused rows, and empty sheets prevents file bloat from creeping in over time.
- Compress images right away. Adding images without compression may not seem like a problem at first, but over time it adds up quickly.
- Store raw data elsewhere. Keeping massive datasets in a database or external file ensures your working spreadsheet stays light and responsive.
- Keep backups. Even well-maintained files can run into trouble. Regular backups guarantee you’ll never lose your work to corruption or file errors.
Conclusion
Excel files that are too big can cause frustration, from lag and crashes to complete failure to open. The good news is that with a mix of smart file management and repair tools, you can keep your spreadsheets running smoothly. Simple fixes like reducing formatting, compressing images, or splitting files go a long way. And if corruption strikes, Repairit Excel File Repair can bring your data back safely.
By staying proactive with your file management, you’ll save yourself time and avoid stress.
FAQs
-
1. What is the maximum file size Excel can handle?
Excel supports files up to 2GB, but performance usually drops before reaching that limit. In most cases, the slowdown starts when the file has too many formulas, links, or objects, even if it’s smaller than 1GB. The version of Excel and the computer’s memory also affect how well a large file runs. -
2. Does saving as .xlsx always make Excel files smaller?
Yes, .xlsx format uses compression, which normally reduces file size compared to .xls. However, the difference depends on the type of content inside the file. Files with heavy images or complex formatting may not shrink much, while files with mostly data and formulas usually compress well. -
3. Is Google Sheets better for large Excel files?
Google Sheets works for small to medium files, but it has stricter limits than Excel. The platform has a 10 million cell limit, and performance may drop with very detailed spreadsheets. It’s more useful for collaboration and quick edits rather than handling very heavy datasets.


 ChatGPT
ChatGPT
 Perplexity
Perplexity
 Google AI Mode
Google AI Mode
 Grok
Grok